At Dr Tayyab saleem malik clinic (Cosmetic Enclave)
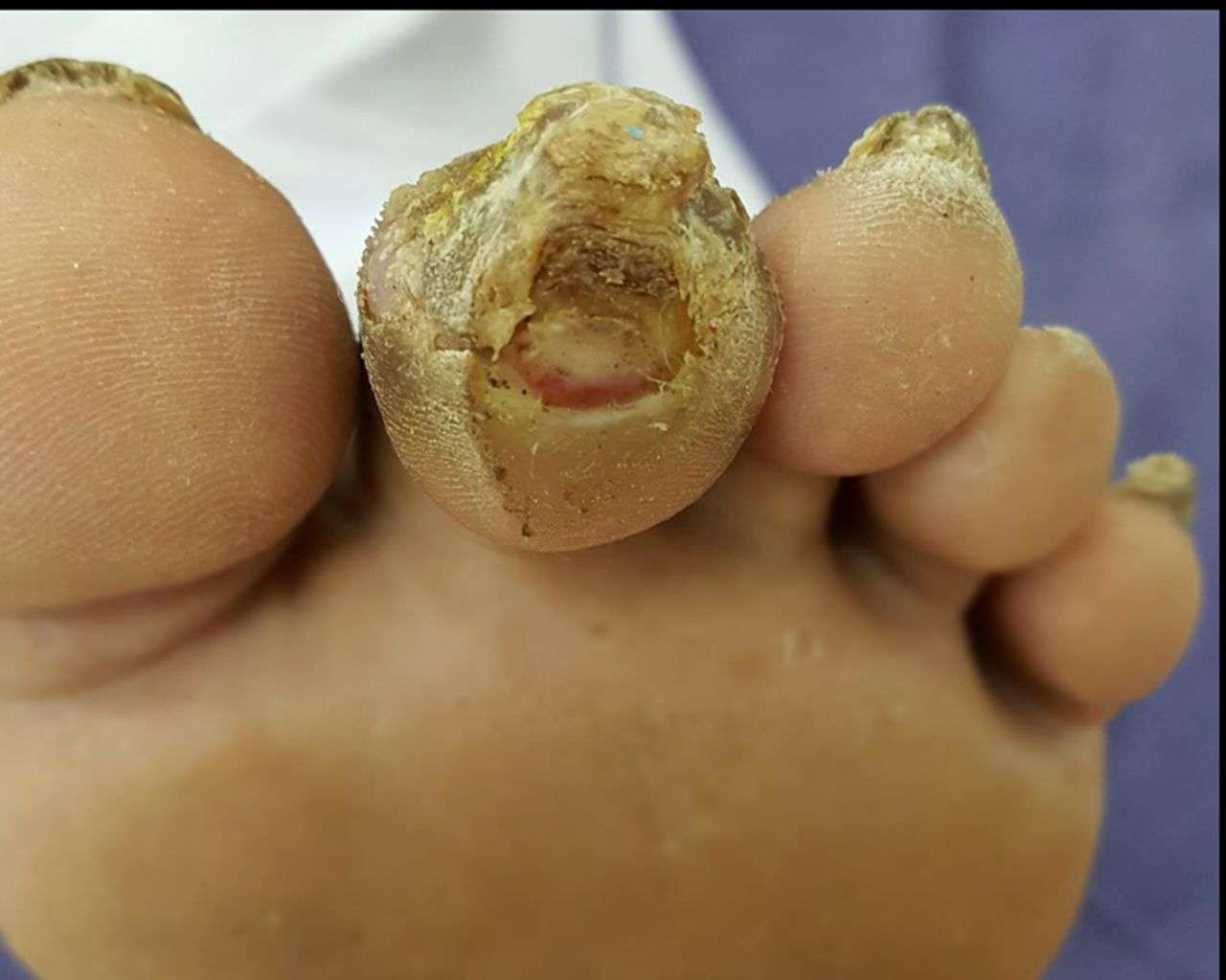
Diabetic foot refers to a range of foot-related complications that can occur as a result of diabetes. Diabetes can cause damage to the nerves (neuropathy) and impair blood flow to the lower extremities (peripheral arterial disease), leading to various foot problems. These issues can be serious and may increase the risk of foot ulcers, infections, and even amputations if not properly managed.
Here are some common aspects and considerations related to diabetic foot:
- Neuropathy: Diabetes-related nerve damage can lead to loss of sensation in the feet, making it difficult to detect injuries or trauma. Reduced sensation can also affect foot alignment and coordination, leading to pressure points and deformities.
- Peripheral arterial disease (PAD): Diabetes can affect blood vessels, leading to poor circulation in the lower extremities. Reduced blood flow impairs wound healing and increases the risk of infection.
- Foot ulcers: Due to reduced sensation and poor blood circulation, small cuts, blisters, or injuries can go unnoticed and develop into ulcers. Diabetic foot ulcers are slow to heal and are prone to infection.
- Infections: Diabetic foot ulcers can become infected easily due to the compromised immune response and reduced blood flow. Infections can spread rapidly and may require aggressive treatment to prevent complications.
- Charcot foot: Charcot foot is a condition characterized by weakened bones and joint deformities in the foot. It can occur in individuals with diabetic neuropathy who continue to walk on an injured foot, leading to progressive bone damage and deformity.
Managing diabetic foot requires a comprehensive approach involving healthcare professionals specializing in diabetes, wound care, podiatry, and vascular health. Here are some key aspects of diabetic foot care:
- Regular foot examinations: Routine foot examinations are essential to assess sensation, circulation, and detect any early signs of foot problems. This includes checking for changes in skin color, temperature, sensation, and evaluating foot deformities.
- Footwear and foot hygiene: Proper footwear that provides support, cushioning, and protection is crucial for individuals with diabetic foot. Regular foot hygiene, including washing and thoroughly drying the feet, helps prevent infections.
- Blood sugar control: Maintaining good blood sugar control plays a significant role in reducing the risk of complications and promoting wound healing.
- Wound care: Proper wound care is essential for diabetic foot ulcers. This includes cleaning the wound, removing dead tissue (debridement), applying appropriate dressings, and offloading pressure from the affected area.
- Offloading: Reducing pressure on foot ulcers or high-pressure areas is vital for healing. This can be achieved through the use of orthotic devices, specialized footwear, or casts.
- Infection management: Prompt identification and treatment of infections are critical to prevent their spread. This may involve the use of antibiotics, wound cultures, and, in severe cases, hospitalization.
- Vascular assessment: Assessment of blood flow to the lower extremities helps identify any arterial blockages or circulation issues. Vascular interventions, such as angioplasty or bypass surgery, may be necessary in some cases.
Diabetic foot requires ongoing care, regular monitoring, and collaboration with healthcare professionals to prevent complications and promote optimal foot health. It is important for individuals with diabetes to be proactive in their foot care and seek medical attention promptly for any concerns or issues related to their feet.