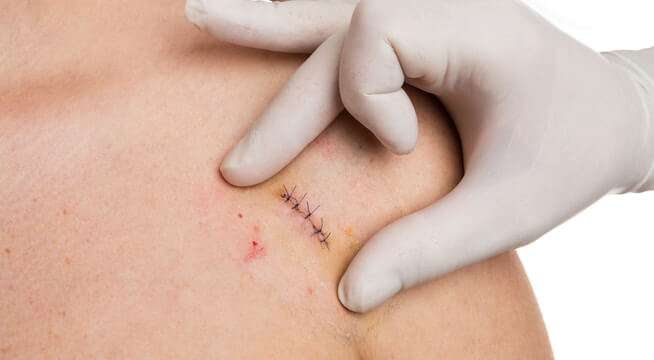
At Dr Tayyab saleem malik clinic (Cosmetic Enclave).Wounds refer to any injury or damage to the skin, underlying tissues, or organs of the body. They can result from a variety of causes, such as accidents, trauma, surgical procedures, or underlying medical conditions. Here are some important points about wounds:
- Types of Wounds: Wounds can be classified into different types based on their characteristics and causes. Common types of wounds include:
- Incised Wounds: Caused by a sharp object, resulting in a clean, straight cut.
- Lacerations: Irregular, jagged wounds caused by a tearing or crushing force.
- Puncture Wounds: Caused by a pointed object, such as a nail or needle, piercing the skin.
- Abrasions: Superficial wounds that occur when the skin is scraped or rubbed against a rough surface.
- Avulsions: Wounds where a portion of tissue is forcibly torn away, often resulting in a flap or hanging tissue.
- Contusions: Bruises caused by blunt force trauma, resulting in damaged blood vessels and discoloration of the skin.
- Wound Healing Process: The human body has a remarkable ability to heal wounds. The healing process typically involves four overlapping stages:
- Hemostasis: The body initiates the formation of blood clots to stop bleeding and create a temporary seal over the wound.
- Inflammation: The body’s immune response kicks in, clearing away debris and fighting off potential infections.
- Proliferation: New blood vessels form, and the wound is rebuilt with the production of collagen, granulation tissue, and epithelial cells.
- Remodeling: The newly formed tissue gradually strengthens and reorganizes to improve the wound’s strength and flexibility.
- Wound Care and Management: Proper wound care is essential to promote healing and reduce the risk of complications. Treatment may include:
- Cleaning: Thoroughly cleaning the wound with mild soap and water or a sterile saline solution to remove debris and bacteria.
- Dressings: Applying appropriate wound dressings to protect the wound, promote a moist healing environment, and prevent infection.
- Antibiotics: In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent or treat wound infections.
- Closure: Depending on the type and severity of the wound, closure methods may include stitches, staples, adhesive tapes, or surgical techniques.
- Follow-up Care: Regular monitoring of the wound, changing dressings as needed, and seeking medical attention if any signs of infection or complications arise.
- Complications: If wounds are not properly managed or if underlying medical conditions are present, complications may occur. These can include infection, delayed wound healing, excessive scar formation (keloids), and the development of chronic wounds.
It’s important to note that the management of wounds should be individualized based on the specific characteristics and needs of each individual. Proper wound care, timely medical attention, and adherence to healthcare professionals’ recommendations can significantly aid the healing process and minimize complications.