At Dr. Tayyab saleem malik clinic (Cosmetic Enclave)
Hand fractures are common injuries that involve a break or crack in one or more of the bones in the hand. These fractures can occur from various causes, including falls, sports injuries, direct impact, or repetitive stress. The hand is composed of multiple bones, including the metacarpal bones in the palm and the phalanges in the fingers.
There are different types of hand fractures, and the treatment approach depends on the location, severity, and stability of the fracture. Here are some common types of hand fractures:
- Boxer’s fracture: This fracture involves the neck of the metacarpal bone, typically the fifth metacarpal, which connects to the small finger. It often results from punching or striking an object forcefully.
- Phalanx fractures: These fractures occur in the phalanges, which are the bones of the fingers. They can involve the proximal, middle, or distal phalanges and may result from crushing injuries, direct trauma, or twisting motions.
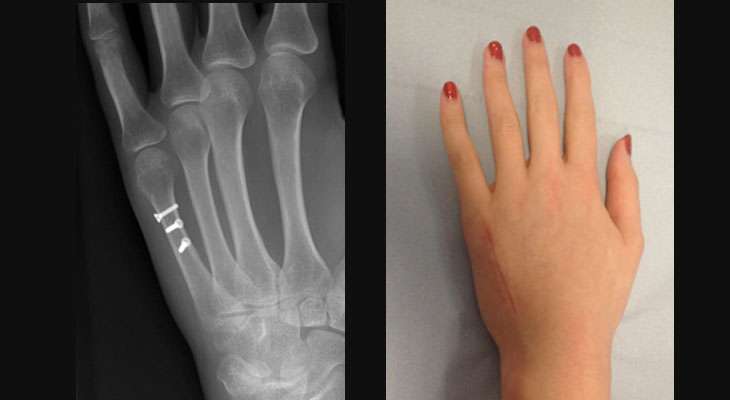
- Metacarpal fractures: Fractures can occur in any of the metacarpal bones. The severity and treatment depend on factors such as the location of the fracture (base, shaft, or neck) and whether it is displaced (bones separated) or non-displaced (bones still aligned).
- Fracture-dislocations: These injuries involve both a fracture and a dislocation of a joint in the hand. Fracture-dislocations can cause significant damage to the surrounding structures and often require surgical intervention.
The symptoms of hand fractures may include pain, swelling, tenderness, deformity, difficulty moving the hand or fingers, and bruising. If you suspect a hand fracture, it is essential to seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Treatment options for hand fractures can vary and may include:
- Immobilization: Stable fractures or non-displaced fractures may be treated with a cast, splint, or custom orthosis to immobilize the hand and promote healing.
- Closed reduction: If the fracture is displaced, a healthcare professional may manipulate the bones back into alignment without surgery. This is known as a closed reduction and may be performed under local or general anesthesia.
- Open reduction and internal fixation: For complex or unstable fractures, surgical intervention may be necessary. The surgeon will realign the bones and use metal pins, screws, plates, or wires to hold them in place while they heal.
Following treatment, rehabilitation and physical therapy may be recommended to restore strength, flexibility, and function to the hand. Exercises may focus on improving range of motion, grip strength, and dexterity.
It is important to follow the instructions of the healthcare professional, including keeping the hand elevated, taking prescribed pain medications, and attending follow-up appointments for monitoring and evaluation of the healing process.
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment of hand fractures are crucial to ensure proper healing and minimize complications. If you suspect a hand fracture, seek prompt medical attention from a healthcare professional specializing in orthopedic injuries or hand surgery. They can provide a comprehensive evaluation, order diagnostic tests if needed, and develop a personalized treatment plan for your specific injury.