At Dr.Tayyab saleem malik clinic (Cosmetic Enclave)
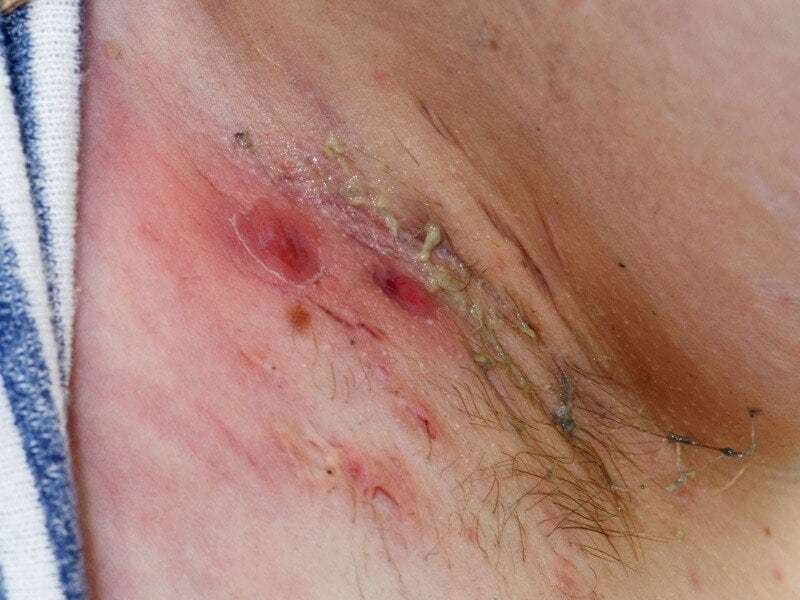
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), also known as acne inversa, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that primarily affects the areas of the body with apocrine sweat glands, such as the armpits, groin, buttocks, and under the breasts. HS is characterized by recurrent, painful, and inflamed nodules, abscesses, and draining sinus tracts in these areas.
The exact cause of hidradenitis suppurativa is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, hormonal, and immune system factors. Risk factors for developing HS include family history, obesity, smoking, and hormonal imbalances.
The symptoms of HS can vary in severity and may include:
- Painful, deep-seated nodules or abscesses: These can be tender and painful and may fluctuate in size. They often recur and can lead to the formation of sinus tracts or tunnels under the skin.
- Open, draining sores: The nodules or abscesses may rupture and release pus or blood, resulting in open wounds that can be slow to heal.
- Scarring and skin changes: Over time, repeated episodes of inflammation and healing can lead to thickened, scarred skin in the affected areas.
- Restricted mobility: In severe cases, HS can cause pain and discomfort that limit movement and impact daily activities.
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a chronic condition, and management aims to control symptoms, prevent flare-ups, and promote healing. Treatment options may include:
- Topical treatments: Mild cases of HS may be treated with topical medications, such as antibiotics, retinoids, or anti-inflammatory creams, to reduce inflammation and control infection.
- Systemic medications: For moderate to severe cases, oral medications, such as antibiotics, hormonal therapies (e.g., oral contraceptives or anti-androgens), or immune-modulating drugs may be prescribed to manage inflammation and prevent new lesions.
- Intralesional injections: For individual nodules or abscesses, injections of corticosteroids or other medications may be used to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Wound care: Proper wound care and hygiene are essential to prevent infection and promote healing of open sores. This may include regular cleansing, dressings, and the use of topical antiseptics.
- Surgical interventions: In some cases, surgical procedures may be necessary. This can involve draining or removing abs