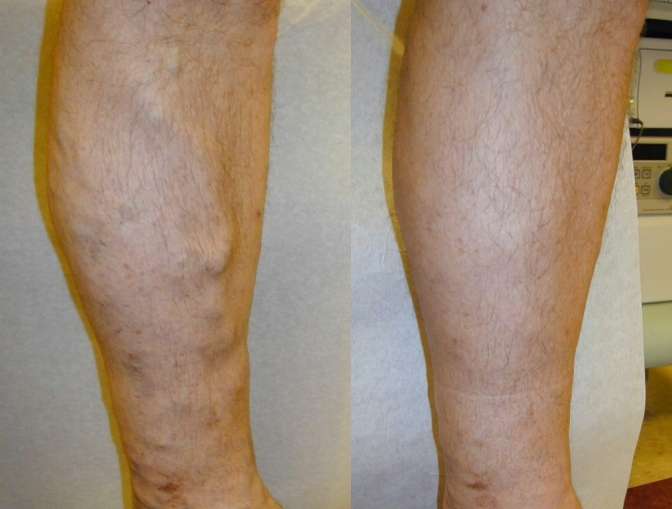
At Dr. Tayyab saleem malik clinic (Cosmetic Enclave)
A non-healing ulcer, also known as a chronic ulcer, is a type of wound that fails to progress through the normal stages of healing within the expected timeframe. These ulcers can be a result of various underlying factors and often require specialized care for proper healing.
Non-healing ulcers can occur for several reasons, including:
-
Poor blood circulation: Conditions such as peripheral artery disease (PAD), venous insufficiency, or diabetes can impair blood flow to the affected area. Inadequate blood supply slows down the healing process and increases the risk of ulceration.
-
Pressure or repetitive trauma: Prolonged pressure or repetitive friction on a particular area, commonly seen in bedridden or wheelchair-bound individuals, can lead to the formation of pressure ulcers or chronic wounds that do not heal properly.
-
Infection: Persistent or recurrent infections can hinder the healing process and contribute to the development of non-healing ulcers. Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can delay wound healing and require appropriate treatment.
-
Underlying medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, autoimmune disorders, or peripheral neuropathy, can compromise the body’s ability to heal wounds effectively. These conditions often result in chronic ulcers that require specialized care.
-
Nutritional deficiencies: Inadequate nutrition, particularly a lack of essential vitamins and minerals, can impair wound healing. Poor intake of protein, vitamin C, zinc, and other nutrients necessary for tissue repair can contribute to the formation of non-healing ulcers.
The management of non-healing ulcers typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, involving healthcare professionals such as wound care specialists, vascular surgeons, podiatrists, or infectious disease specialists. Treatment may include:
-
Wound debridement: Removing dead or infected tissue from the wound to promote healing and prevent further complications.
-
Infection control: Managing and treating any underlying infections through the use of antimicrobial dressings, topical or systemic antibiotics, or other appropriate interventions.
-
Offloading and pressure redistribution: For pressure ulcers, relieving pressure on the affected area through the use of specialized cushions, mattresses, or braces is essential to facilitate healing.
-
Enhancing blood circulation: Addressing underlying circulation issues through lifestyle modifications, medications, or surgical interventions can help improve blood flow to the wound site.
-
Wound dressings and advanced therapies: Utilizing appropriate dressings, such as moist wound healing dressings or advanced therapies like negative pressure wound therapy or growth factor applications, can aid in wound healing.
-
Nutritional support: Ensuring proper nutrition through a balanced diet or nutritional supplements can provide the essential nutrients needed for optimal wound healing.
It is important to seek medical attention for a non-healing ulcer, as these wounds can lead to severe complications if left untreated. A healthcare professional can assess the wound, identify underlying causes, and develop a tailored treatment plan to promote healing and prevent further progression.