At Dr. Tayyab saleem malik clinic (Cosmetic Enclave)
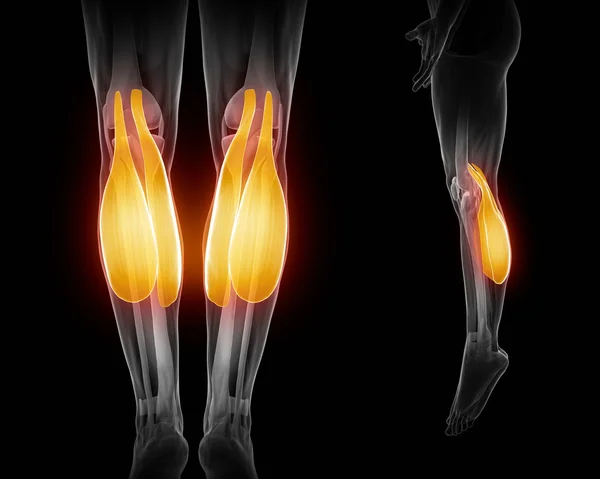
Tendon injuries occur when there is damage or trauma to the tendons, which are thick bands of fibrous tissue that connect muscles to bones. These injuries can result from various causes, such as overuse, repetitive motions, sudden forceful movements, or direct trauma.
Tendon injuries are classified based on the extent and severity of the damage. Here are two common types:
- Tendonitis: Tendonitis, also known as tendinitis, refers to inflammation of a tendon. It often occurs due to overuse or repetitive motions that put strain on the tendon. Tendonitis commonly affects tendons in the shoulders, elbows, wrists, knees, or ankles. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, tenderness, and limited range of motion.
- Tendon Tears or Ruptures: Tendon tears or ruptures involve a partial or complete tear in the tendon. These injuries can occur suddenly from a forceful impact or develop gradually due to chronic degeneration or wear and tear. Tendon tears can cause severe pain, swelling, weakness, and difficulty moving the affected joint.
The treatment for tendon injuries depends on the type, location, and severity of the injury. Here are some approaches:
- Rest and Immobilization: Resting the affected tendon and immobilizing the joint with splints, braces, or casts can help reduce stress and allow the tendon to heal. Immobilization is typically used in cases of tendonitis or partial tears.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy plays a crucial role in rehabilitating tendon injuries. Therapeutic exercises, stretches, and modalities are employed to improve range of motion, strengthen the muscles around the tendon, and promote healing.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be recommended to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation associated with tendonitis. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be used to relieve severe pain and inflammation, but their use is limited to specific circumstances.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy involves injecting a concentrated solution of the patient’s own platelets, rich in growth factors, into the injured tendon. This treatment aims to stimulate tissue healing and promote regeneration.
- Surgical Intervention: In cases of severe tendon tears or complete ruptures, surgical repair may be necessary. The procedure may involve suturing the torn ends of the tendon or using grafts or anchors to reattach the tendon to the bone. Rehabilitation following surgery is typically essential to restore strength and function.
The recovery and prognosis for tendon injuries vary depending on the extent of the injury, location, and individual factors. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment play a crucial role in optimizing outcomes and minimizing complications. It is important to seek medical attention from a healthcare professional, such as an orthopedic specialist or a sports medicine physician, for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan tailored to your specific condition.
Prevention strategies for tendon injuries include gradually increasing the intensity and duration of physical activities, using proper techniques and equipment, warming up before exercise, and incorporating rest and recovery periods into training routines. Listening to your body and addressing any signs of pain or discomfort promptly can help prevent further damage to the tendons.
If you suspect a tendon injury or experience symptoms suggestive of a tendon problem, consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in musculoskeletal injuries. They can provide a comprehensive evaluation, recommend appropriate diagnostic tests, and develop a personalized treatment plan to facilitate healing and restore function.