At Dr. Tayyab saleem malik clinic (Cosmetic Enclave)
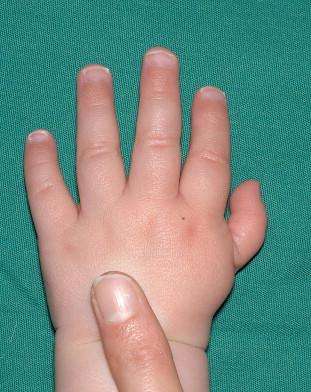
Thumb hypoplasia is a congenital condition characterized by underdevelopment or incomplete formation of the thumb. It is typically present from birth and can vary in severity, ranging from mild thumb abnormalities to a complete absence of the thumb. Here are some key points about thumb hypoplasia:
- Causes: The exact cause of thumb hypoplasia is often unknown. It can occur sporadically or be associated with genetic or chromosomal abnormalities. Some cases may be linked to certain environmental factors or prenatal exposures. Thumb hypoplasia can also be seen in the context of syndromes such as Holt-Oram syndrome or VACTERL association.
- Classification: Thumb hypoplasia is classified into different types based on the level of thumb involvement and the presence of associated hand abnormalities. The classification system commonly used is the Blauth classification, which categorizes thumb hypoplasia into five types (Type I to Type V) based on the level of bone involvement and the presence of joints.
- Manifestations: Thumb hypoplasia can present in various forms, including:
- Shortened thumb: The thumb is smaller in size than normal but still retains some functionality.
- Hypoplastic thumb: The thumb is underdeveloped and may have abnormalities in its structure, such as missing bones or joint deformities.
- Absent thumb: The thumb is completely absent, and the hand may have other compensatory structures or fingers that take on thumb-like functions.
- Functional Implications: Thumb hypoplasia can significantly impact hand function and dexterity. The thumb plays a crucial role in grasping objects, manipulating tools, and performing fine motor tasks. The severity of thumb hypoplasia determines the functional limitations and the need for adaptive strategies or interventions.
- Treatment Options: The management of thumb hypoplasia aims to improve hand function and appearance. Treatment options may include:
- Hand therapy: Occupational or physical therapy can help maximize hand function and teach compensatory techniques.
- Orthotic devices: Splints or thumb braces may be used to provide support and improve thumb function.
- Surgical interventions: In more severe cases, surgical procedures like pollicization (reconstructing the thumb using another finger) or toe-to-thumb transfer may be considered to create a functional thumb.
- Prosthetic devices: Customized thumb prostheses can be considered to assist with grasping and daily activities.
The specific treatment approach depends on the individual’s unique condition, functional needs, and overall hand structure. Early intervention and a multidisciplinary approach involving hand surgeons, occupational therapists, and other specialists are crucial for optimizing outcomes and maximizing hand function in individuals with thumb hypoplasia.